Main menu
Common skin conditions
NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author(s): Dr Amanda Oakley, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton New Zealand, 2008; updated by Dr Geetika Seth, Dermatopathology fellow, University of School of Medicine Boston, USA; Dr Sabrina Sapsford, Dermatology Research Fellow, Te Whatu Ora, Counties Manukau; and Dr Libby Whittaker, DermNet Medical Writer, New Zealand (2023)
Reviewing dermatologist: Dr Ian Coulson
Edited by the DermNet content department
Introduction
How it works
Chemicals used
European Standard Series
T.R.U.E.® Test series
North American Standard Series
International Standard Series
Other allergens
Patch tests are used to identify the cause of allergic contact dermatitis. Standard or baseline series of allergens are recommended for people undergoing patch testing because these include the most common and important allergens that cause dermatitis, and will identify over 70% of culprit allergens. Specific allergens may be added or removed from the series as they become more or less frequent culprits.
Additional allergens may also be tested depending on the patient’s medical and social history, the site of their suspected contact dermatitis or occupation.
The specific standard/baseline series may vary by geographical location due to differences in allergens, medicaments and social practices. The European Baseline Series (EBS) is most commonly used in Europe and elsewhere in the world. Other series include the International Standard, North American Baseline, and American Core Allergen; and series specific to other countries such as Belgium, Finland, Sweden, Hungary, Italy, Korea, Australia, and New Zealand.
The Paediatric Baseline Series has also recently been developed to aid the investigation of allergic contact dermatitis in children.
The patch test centre usually orders its allergens from several manufacturers. Most chemicals are mixed in petrolatum and supplied in a syringe. A few chemicals are dissolved in water and supplied in a bottle. The patches consist of hypoallergenic adhesive paper with up to ten chambers. The chambers are made of metal or plastic and are round or square.
The chemicals have been tested to determine the most suitable concentration for testing. If too weak, some people who are allergic to the chemical will not react to the test substance (false negative). If too strong, some people who are not allergic to the chemical will have an irritant reaction (false positive).
A small amount of each petrolatum-based allergen is carefully squeezed into a chamber. Liquid allergen solutions are dropped onto the filter paper placed in the test chamber. Two or three completed patch test panels each with 10-12 allergens applied are fixed to the skin of the upper back. Each patch is carefully numbered or labelled so the allergen in each chamber can be correctly identified.
The patches are generally left in place for 48 hours. The dermatologist will inspect the test site after they have been removed and at least once more, usually 48 hours later.

Baseline series of patch test allergens

Using IQ chambers

Applying liquid for patch testing
The Thin-layer Rapid-Use Epicutaneous (T.R.U.E.®) Test series is already prepared; the backing paper is removed and the patches are carefully applied to the patient’s back.

Baseline series of patch test allergens

Baseline series of patch test allergens

Baseline series of patch test allergens
The chemicals in the baseline series depend on which series is being used. The European Baseline Series (updated 2023) is described below. Most test substances are single compounds but some of the tests are mixtures of closely-related chemicals.
The European Baseline Series (EBS) includes 32 allergens (see table below), with another 10 in the extended series (including linalool and limonene hydroperoxides, compositae mix II, diazolidinyl urea, 2-bromo-2-nitropropane-1,3-diol, 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, sorbitan sesquioleate, and sorbitan monooleate).
Allergen |
Concentration % (w/w), in petrolatum (unless stated otherwise) |
Source of dermatitis |
Positive reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
Potassium dichromate |
0.5 |

|
|
p-Phenylenediamine (PPD) |
1.0 |

|
|
Thiuram mix |
1.0 |

|
|
Neomycin sulfate |
20.0 |
Neomycin (antibiotic) |

|
Cobalt chloride |
1.0 |
Cobalt (metal) |

|
Caine mix III |
10.0 |
Benzocaine (local anaesthetic) |

|
Nickel sulfate |
5.0 |
Nickel (metal, coins, jewellery) |

|
2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) |
2.0 |
Adhesives, nail products, dental and orthopaedic materials, UV inks |
|
Colophonium |
20.0 |
Rosin and colophony (adhesive) |

|
Paraben mix |
16.0 |
Parabens (preservative) |

|
N-Isopropyl-N-phenyl-4-phenylenediamine (IPPD) |
0.1 |
Rubber antioxidant, leather shoes, oils and greases |

|
Lanolin alcohol |
30.0 |

|
|
Mercapto mix |
2.0 |

|
|
Epoxy resin |
1.0 |
Epoxy resin (adhesive) |

|
Myroxylon pereirae resin |
25.0 |
Balsam of Peru (fragrance) |

|
4-tert-Butylphenol formaldehyde resin |
1.0 |

|
|
2-mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) |
2.0 |

|
|
Formaldehyde |
2.0 in water |
Formaldehyde and formalin (in clothing, cosmetics, household products) |

|
Fragrance mix I (cinnamic alcohol, cinnamic aldehyde, hydroxycitronellal, amylcinnamaldehyde, geraniol, eugenol, isoeugenol, oakmoss absolute) |
8.0 (Sorbitan sesquioleate 5% emulsifier) |

|
|
Sesquiterpene lactone mix (alantolactone, dehydroxosus lactone, costunolide) |
0.1 |
Compositae allergy (daisies) |
|
1.0 |
Preservative in foods, pharmaceuticals, and other products |
||
10 |
Resinous mixture produced by bees, used in a variety of both oral and topical agents, cosmetics, and mouthwashes |
||
Cl+Me-isothiazolinone (Kathon) / methylchloroisothiazolinone + methylisothiazolinone (MCI/MI) |
0.02 in water |
Isothiazolinone (preservative) |

|
Budesonide |
0.01 |

|
|
Tixocortol pivalate |
0.1 |

|
|
0.5 |
Formaldehyde-releasing preservative |

|
|
Fragrance mix II (lyral, citral, farnesol, citronellol, hexyl cinnamic aldehyde, coumarin) |
14 |

|
|
Hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde (Lyral) |
5.0 |
Fragrance ingredient used in perfumes, soaps, cosmetics |
|
0.2 in water |
Preservative |

|
|
0.1 |
Industrial preservative used in inks, paints, varnishes, adhesives, cleaning products, and cooling fluids |
||
Textile dye mix |
6.6 |

|
|
Decyl glucoside |
5.0 |
Surfactant found in many cleansers and cleaning products |
Compared to the European Baseline Series, at the time of writing the T.R.U.E.® Test allergens do not include 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, IPPD, sesquiterpene lactone mix, sodium metabisulfite, propolis, fragrance mix II, Lyral, methylisothiazolinone, benzisothiazolinone, textile dye mix, or decyl glucoside. The three test panels comprise 35 allergens, including the following:
Allergen |
Concentration mg/cm2 in stated vehicle |
Source of dermatitis |
Positive reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
Carba mix |
0.25 in hydroxypropyl cellulose |
Rubber antioxidant |

|
Ethylenediamine dihydrochloride |
0.05 in methyl-cellulose |
Ethylenediamine (preservative) |

|
Thiomersal |
0.007 in hydroxypropyl cellulose |
Thiomersal (mercurial preservative) |

|
Diazolidinyl urea |
0.55 in povidone |
Formaldehyde-releasing preservative |

|
Imidazolidinyl urea |
0.60 in povidone |
Imidazolidinyl urea (preservative) |

|
Hydrocortisone-17-butyrate |
0.02 in povidone |

|
|
2-Bromo-2-nitropropane-l,3-diol (Bronopol) |
0.25 in povidone |
Formaldehyde-releasing preservative |

|
0.6 in hydroxypropyl cellulose |
Antibiotic (topical medication |

|
|
Disperse Blue 106 |
0.05 in povidone |

|
|
Parthenolide (feverfew) |
0.003 in povidone |

|
|
Gold sodium thiosulphate |
0.075 in hydroxypropyl cellulose |
Metal see Gold |
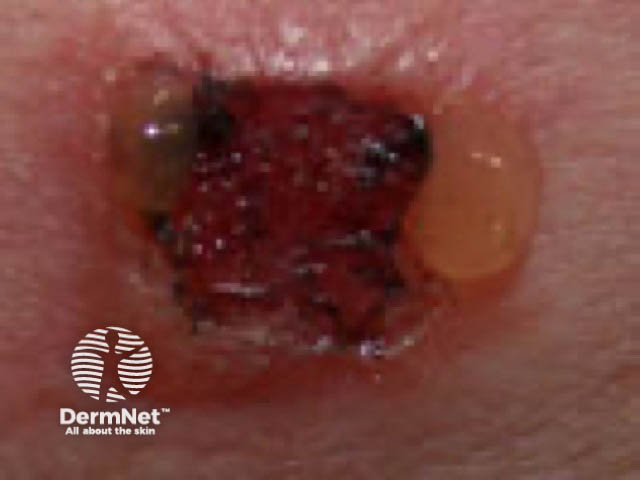
 Positive patch test to gold sodium thiosulphate |
Quaternium-15 (Dowicil 200) |
1.0 in hydroxypropyl cellulose |
Quaternium-15 (preservative) |

|
Black rubber mix |
0.075 in povidone |
Rubber products (eg, tires, sporting equipment, goggles, shoes) |
|
Quinoline mix (including clioquinol) |
0.19 in povidone |
The North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) Baseline Series includes a greater range of allergens (50 baseline allergens, or extended versions with 65 or 80 allergens). It does not include thiomersal. Some of the other allergens in the NACDG series are shown below.
Allergen |
Concentration % (w/w) in petrolatum |
Source of dermatitis |
Positive reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
DMDM Hydantoin |
1.0 |
Formaldehyde-releasing preservative |
|
Bacitracin |
20.0 |
Antibiotic |

|
Mixed dialkyl thiourea |
1.0 |
Rubber antioxidant, photographic fixing, resins, photocopy paper. |

|
Glutaraldehyde |
0.5 |
A preservative used for sterilisation, embalming, tanning leather. |

|
2-Bromo-2-nitropropane-l,3-diol (Bronopol) |
0.5 |
Formaldehyde-releasing preservative |

|
Propylene glycol |
30.0 in water |
A vehicle in medications, cosmetics, foods. |
|
2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone (Benzophenone 3) |
10.0 |
Sunscreen |

|
4-Chloro-3,5-xylenol (PCMX) |
1.0 |
Preservative |
|
Ethyleneurea, melamine formaldehyde mix |
5.0 |
Formaldehyde type of textile resin |

|
Iodopropynyl butylcarbamate (Glycasil™) |
0.2 |
Preservative for wood, paint, cooling fluids, cosmetics. |
|
Disperse Blue 106/124 Mix |
1.0 |
Textile dye |

|
Ethyl acrylate |
0.1 |
An acrylic monomer used in adhesives and coatings |

|
Glyceryl monothioglycolate (GMTG) |
1.0 |
Acid perming solution |

|
Toluenesulfonamide formaldehyde resin |
10.0 |
A synthetic resin in lacquers and adhesives (nail cosmetics) |

|
Methyl methacrylate |
2.0 |
Methacrylic monomer in plastics for dentures, artificial nails |

|
Compositae mix II |
5.0 |
Tanacetum vulgare (ragweed), Arnica montana (arnica), Parthenolide (feverfew), Chamomilla romana (chamomile), Achillea millefolium (yarrow) |

|
Cocamidopropylbetaine |
1.0 in water |
Surfactant, detergent |
|
Amerchol L-101 |
5.0 |
Lanolin |
|
Cinnamal |
1.0 |
Fragrance, cinnamon, spices |
A core allergen series with 80 allergens was released by the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS) in 2013, with subsequent updates in 2017 and 2020. Currently there are 90 allergens listed, available in 9 panels. These are intended to be used as a way to logically extend testing for patients beyond the T.R.U.E.® Test, scaling testing up or down depending on the patient and context. More recent additions in 2020 include:
Allergen |
Concentration (%) in petrolatum (unless stated otherwise) |
Source of dermatitis |
|---|---|---|
Peppermint oil |
2.0 |
|
Jasmine absolute oil |
2.0 |
Essential oil |
20.0 in alcohol |
Resin used as food glaze, furniture sealant, and in cosmetics |
|
Carmine |
2.5 |
Food additive, colouring agent |
Lauryl polyglucose (ie, lauryl glucoside |
3.0 |
Surfactant used in products such as shampoo, cosmetics, sunscreens, and deodorants |
10.0 |
Cosmetics |
In comparison to the European Baseline Series, the International Standard Series (with 30 allergens) from the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group (ICDRG) does not contain caine mix, sodium metabisulfite, and benzisothiazolinone. The 0.2% methylisothiazolinone (MI) test and 0.01–0.02% methylchloroisothiazolinone + methylisothiazolinone (MCI/MI) tests have been replaced by a single 0.215% MCI/MI test, following a study (Isaksson et al, 2021) showing the 0.215% mix was superior in detecting patients with MCI/MI contact allergy than the other tests combined.
The expanded International Comprehensive Series contains 80 allergens.
In 2020, patch testing practice in New Zealand was reviewed and the need for national surveillance and identification of relevant allergens was identified. In 2021, the New Zealand Baseline Series (NZBS) was developed by a national panel of dermatologists using a large body of retrospective data. This is the most up-to-date series for the New Zealand population.
There are 30 allergens in the NZBS and another 30 in the extended series, including many from the EBS and the NACDG Baseline Series. Other allergens include:
Allergen |
Concentration (%) and vehicle (petrolatum unless stated otherwise) |
Source of dermatitis |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
Fragrance ingredient |
|
Tea tree oil oxidised |
5.0 |
|
0.1 in water |
Antiseptics, cleaning products |
|
0.3 |
Fragrance ingredient |
Patch testing in the paediatric population has been less extensively studied than in the adult population.
In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the T.R.U.E.® Test for use in children aged 6 to 17.
More recently, the Paediatric Baseline Series (PBS) was published in 2018 based on expert consensus at the American Contact Dermatitis Society meeting. The PBS includes 38 allergens, with 2 blank ‘what else’ spots for other allergens as appropriate. It has been found to be superior in picking up positive patch test results than the T.R.U.E.® Test, which unlike the PBS does not include the following important contact allergens in children:
An Australian Paediatric Baseline Series was also subsequently proposed in 2020.
There are numerous other chemicals that have been reported to cause contact allergy occasionally. About 15% of patients who have positive reactions at patch testing react to an allergen that is not in the baseline series. These allergens are detected using other series of allergens or individual standardised chemicals that have been selected by the dermatologist based on history taking and potential exposures.
Several series have been developed for patients who present with dermatitis on specific sites of the body or for those with certain occupations (eg, Hairdressing Series, Dental Screening) or other risk factors (eg, Shoe or Cosmetic Series).
Atopy patch tests are sometimes undertaken in patients with atopic dermatitis where there is suspicion of exacerbation by a type 1 allergen such as a food allergen or house dust mite.
Sometimes patients may be strongly positive to an allergen with which, according to their medical and social history, they have little or no contact. In this case, consort contact allergic dermatitis may also be considered.