What is Majocchi granuloma?
Majocchi granuloma is a deep and persistent suppurative and granulomatous folliculitis (hair follicle infection) caused by fungal infection. Majocchi granuloma is also known as granuloma trichophyticum.
Who gets Majocchi granuloma?
Various forms of tinea are common in males and females worldwide. Majocchi granuloma mostly affects adults. It is common in developing countries. The associated factors leading to deep follicular infection by dermatophyte fungi may include:
- Longstanding, untreated infection
- Tropical climate
- Shaving or other cutaneous trauma
- Topical steroids (resulting in tinea incognito)
- Immunosuppression, for example during chemotherapy or after organ transplantation.
What is the cause of Majocchi granuloma?
Majocchi granuloma is due to disruption of infected hair follicles so that hair shafts and fungi penetrate into the dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
The infection is most often caused by Trichophyton rubrum. Other fungi that may cause Majocchi granuloma include:
- T. mentagrophytes
- T. tonsurans
- T. violaceum
- Epidermophyton floccosum
-
Non-dermatophyte moulds, like Aspergillus and Phoma.
What are the clinical features of Majocchi granuloma?
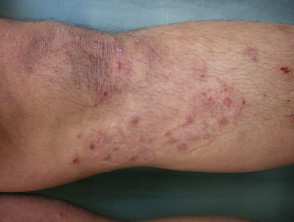
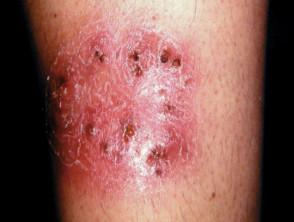
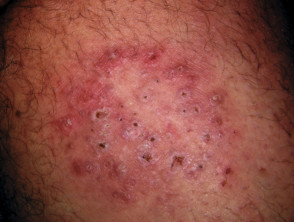
Majocchi granuloma presents with an irregular red, scaly plaque in which there are follicular papules, pustules and nodules. It is usually found on one lower leg.
Evidence for fungal infection may be found in other sites such as scaling on the sole of the foot (tinea pedis) or yellowed, irregular toenails (tinea unguium).
There are two forms of Majocchi granuloma.
- The perifollicular papular form is a localised dermal infection and usually occurs in healthy individuals
- The deep subcutaneous plaque or nodular form arises in people with underlying immunosuppression.
Majocchi granuloma
How is Majocchi granuloma diagnosed?
Suspicion is raised due to the clinical appearance of Majocchi granuloma.
To confirm a fungal infection, scrapings and hair samples may be taken from the affected area for microscopy and fungal culture (mycology). Granulomatous inflammation is found on skin biopsy.
What is the treatment for Majocchi granuloma?
The recommended treatment for Majocchi granuloma is a 4 to 6-week course of oral antifungal agent.
- Terbinafine
- Itraconazole
- Griseofulvin (which is no longer available in New Zealand)
Topical antifungal agents may not be effective due to the deep invasion of the fungus into the hair follicle.