Main menu
Common skin conditions
NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Hon A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, 1999. Updated by Dr Ebtisam Elghblawi, September 2017.
Introduction Demographics Causes Features Diagnosis Differential diagnoses Effect on pregnancy Length of occurence Treatment Recurrence
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy is an itchy, bumpy rash that starts in the stretch marks of the abdomen in the last 3 months of pregnancy then clears with delivery.
It is also called PUPPP or Pruritic Urticarial Papules and Plaques of Pregnancy.
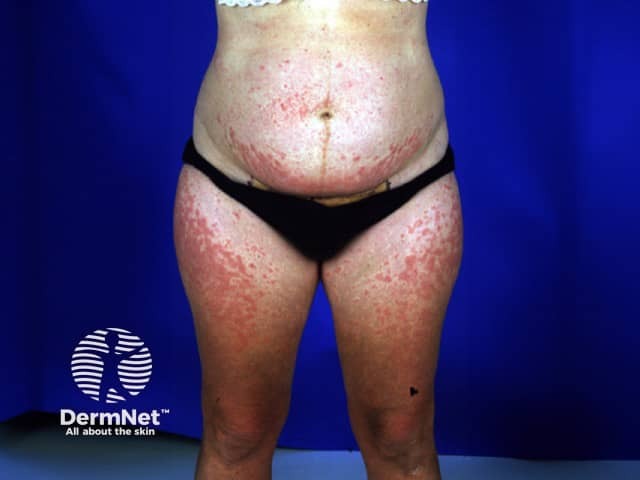
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy PUPPP
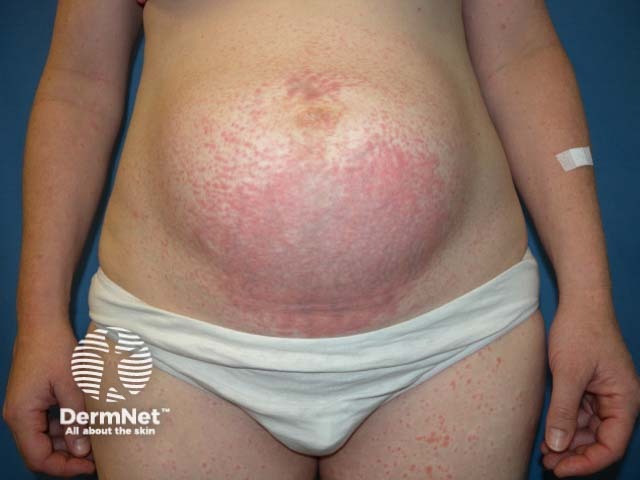
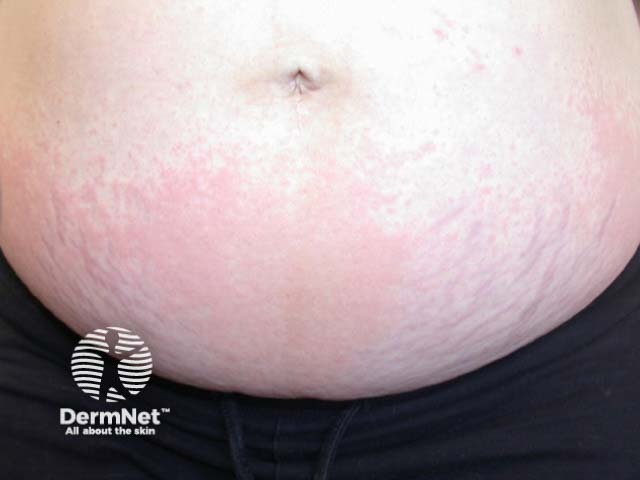
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy occurs in about 1 in 160 pregnancies.
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy is thought to be related to stretching of the skin on the abdomen. The stretching elicits an immune response due to connective tissue damage. Supporting the stretch mark theory are the following observations:
Another theory considers low-level traffic of fetal cells within the mother's circulation, which appears increased in women with polymorphic eruption of pregnancy, and may persist for some time after the baby has been born.
The rash usually begins during the third trimester, in the last few weeks of pregnancy. About 15% of women with polymorphic eruption of pregnancy report that it actually began immediately after delivery.
Small pink papules appear first in the stretch marks around the umbilicus, often with a pale halo around each papule. The papules coalesce to form large, red, urticated (hive-like) plaques, and occasionally small vesicles are present. The rash spreads from the abdomen to involve the buttocks and thighs, and sometimes the arms and legs. Lesions on or above the breasts are rare.
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy is very itchy (pruritic) and patients find it difficult to sleep at night.
The history and clinical findings are usually typical. There are no specific tests. Skin biopsy findings are nonspecific.
Rashes in pregnancy include those that affect non-pregnant women. An itchy rash early in pregnancy is usually caused by prurigo of pregnancy or atopic eczema. When the rash starts in the umbilicus itself or blisters are present, a diagnosis of pemphigoid gestationis may be considered. Skin biopsy is confirmative.
Rarely, the baby can be born with a mild form of polymorphic eruption of pregnancy rash but this soon fades. Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy does not cause any other problem for the baby.
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy continues until delivery then usually resolves within 4–6 weeks. Rarely, it may persist for longer. In some cases, this relates to retained placental products.
There is no curative treatment for polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (apart from delivery!). Symptoms can be controlled using:
It is very uncommon for polymorphic eruption of pregnancy to recur. If it occurs, it is likely to be milder.