Introduction
Patients may present with a skin problem they believe to be confined to the scalp. A full medical and focussed cutaneous history should be followed by brief examination of relevant sites.
The most common scalp symptoms are:
- Itch
- Soreness
- Scale/flaking
- Pustules/sores
Itch may be associated with the majority of skin conditions in the scalp. Soreness is less frequent.
Chronic scaly scalp disorders
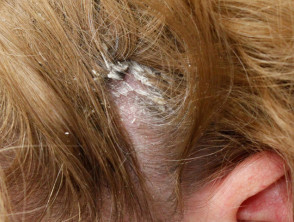
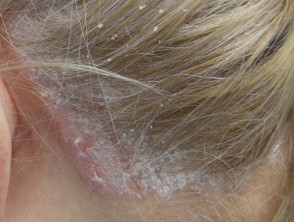
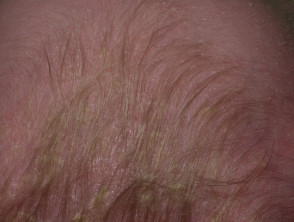
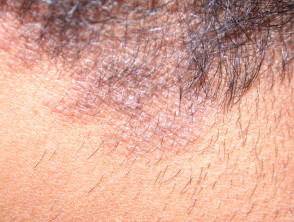
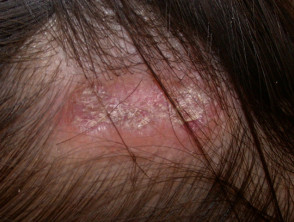
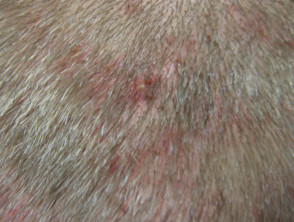
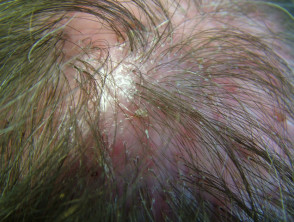
Pityriasis amiantacea
- Very thick asbestos-like scale
- Scale is very adherent to hair shafts
- Subsequent diagnosis usually seborrhoeic dermatitis or psoriasis
Pityriasis amiantacea
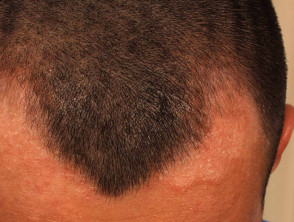
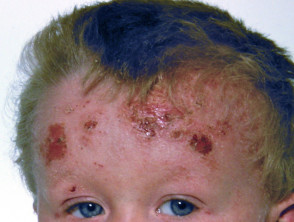
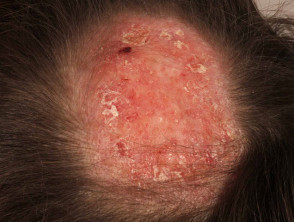
Tinea capitis
- Irregular scaly plaques with moth-eaten hair loss
- May have inflammatory, abscess-like kerion
- Hairs are easy to extract
- Positive microscopy and culture of scrapings and extracted hair
- Sometimes, fluorescence on Wood light examination
Tinea capitis
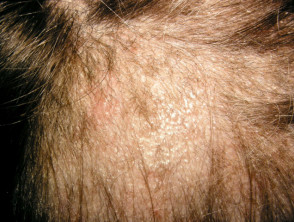
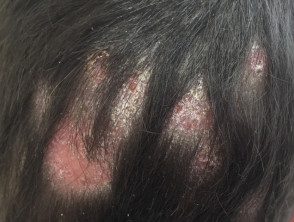
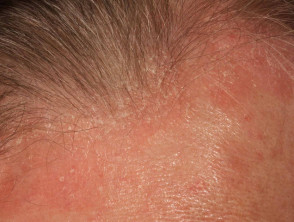
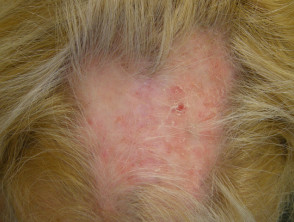
Psoriasis
- Any age, most > 15 years
- May be localised or diffuse
- May be isolated to scalp or involve other body sites
- Check ears, elbows, knees, nails
- Circumscribed erythematous scaly plaques
- Large, usually white scale
- Variable response to topical therapy (various shampoos, calcipotriol, potent topical steroids)
- Hair loss uncommon, but when occurs, loose hair shafts can be extracted from scaly plaques
Scalp psoriasis
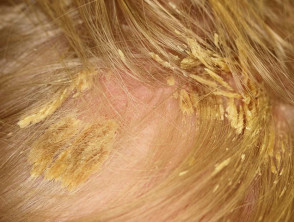
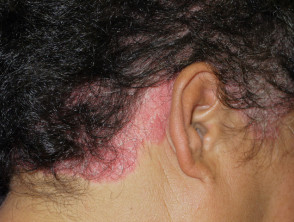
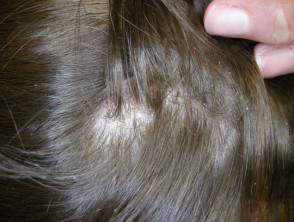
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
- Infants or > 13 years
- May be localised or diffuse
- May be isolated to scalp or involve other body sites
- Check ears, eyebrows, nasolabial folds
- Thin salmon-pink flaky plaques, sometimes annular
- Small flakes of yellow or white scale
- Good, temporary, response to topical therapy (ketoconazole shampoo, mild topical steroid)
- Hair loss uncommon, but when occurs, loose hair shafts can be extracted from secondarily infected, oozy plaques
Seborrhoeic dermatitis of scalp
Atopic dermatitis
- Any age especially children
- In infants, may overlap with seborrhoeic dermatitis
- Usually diffuse and very itchy
- Involves other body sites
- Scalp rash rarely prominent
- Check elbow flexures, popliteal fossae, eyelids
- Ill-defined erythematous blistered or dry plaques
- Lichenification
- Dryness rather than loose scale
- Good response to properly applied topical therapy (potent topical steroid)
- Hair loss rare
Atopic dermatitis of scalp
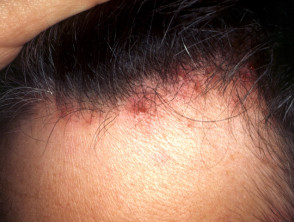
Discoid lupus erythematosus
- Localised erythematous, scaly and hairless, scarred plaques; often multiple
- May be isolated to scalp or involve other body sites
- Check nose, cheeks, ear concha
- Lichen planopilaris
- Localised, sometimes erythematous bald plaques
- Perifollicular scale
- Lonely hairs
Discoid lupus erythematosus of scalp
Chronic pustules and erosions
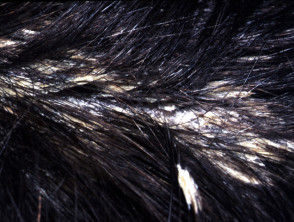
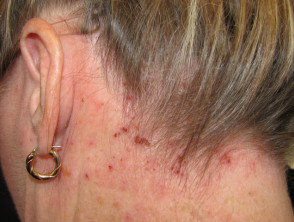
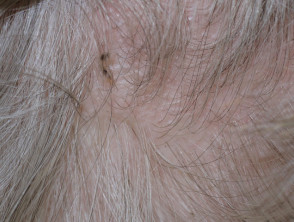
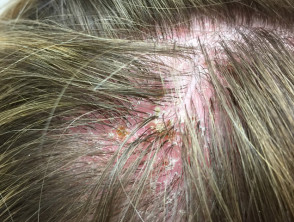
Head lice
- Usually, but not always, young child
- Look for lice on the nape of neck and behind ears
- Nits are adherent white grains on hair shafts
- Red-brown spots on the skin are due to excreted digested blood.
- Excoriations, hair pulled out
Head lice
Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Scalp a common site, also shoulders, buttocks elbows, knees
- Intensely itchy solitary or multiple blisters, rarely seen, as scratched
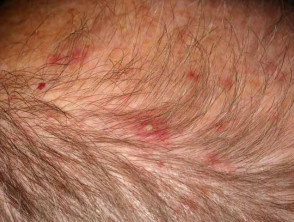
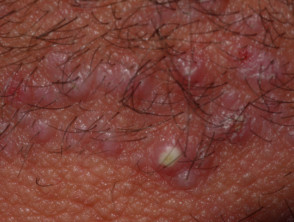
Scalp folliculitis
- Itchy or painful follicular pustules and scratched erosions
- No hair loss
- Poor response to topical steroid
- May improve with long-term oral tetracycline
Scalp folliculitis
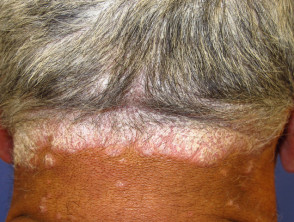
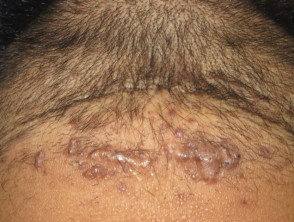
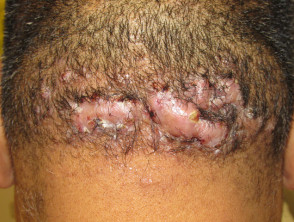
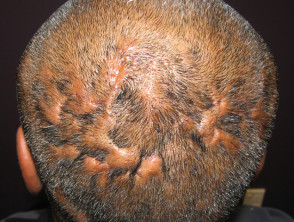
Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae
Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae:
- Males with dark coarse hair
- Occipital scalp
- Few pustules
- Firm follicular papules
- Larger keloid scars with sparse hairs
Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae
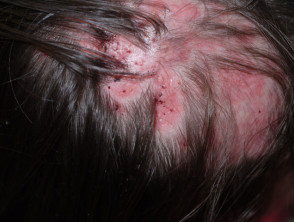
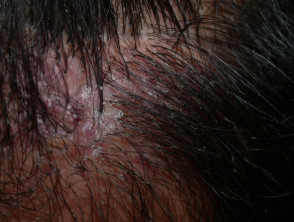
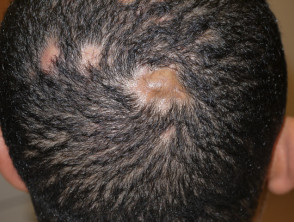
Folliculitis decalvans
- Itchy or painful follicular pustules, perifollicular crusting
- Irregular bald, scarred areas; usually solitary
- May improve with long-term oral tetracycline
Folliculitis decalvans
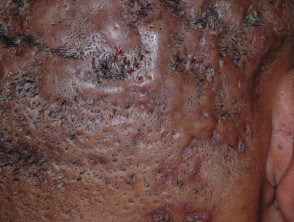
Dissecting cellulitis
- Also known as perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens
- Associated with acne conglobata, hidradenitis suppurativa
- Crusting, inflammatory nodules, large fluctuant cysts, with hair loss
Dissecting cellulitis
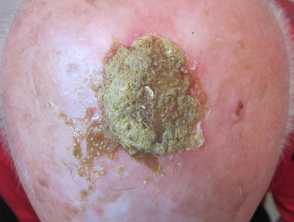
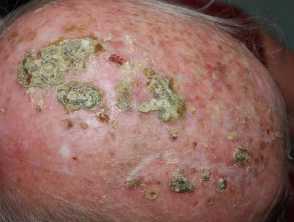
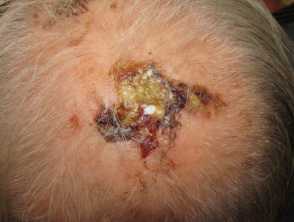
Erosive pustular dermatosis
- Elderly, sun damaged, bald or very thin hair
- One or more masses of greenish pus
- There may be underlying keratotic plaques
- Arise within actinic keratoses or squamous cell carcinoma
Erosive pustular dermatosis