What is nodulocystic acne?
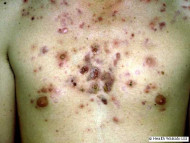
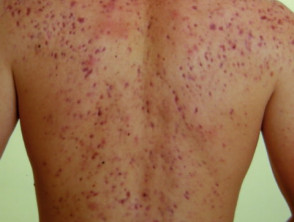
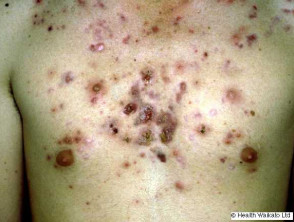
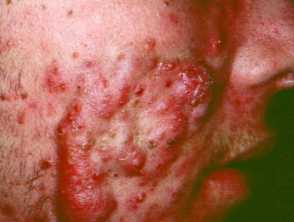
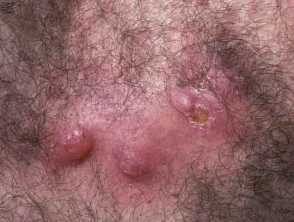
Nodulocystic acne is a severe form of acne affecting the face and upper trunk, characterised by nodules and cysts that typically resolve with scarring.
Nodulocystic acne of the face and upper trunk
Who gets nodulocystic acne?
Nodulocystic acne is usually a disorder of adolescence and early adult life seen most commonly in males. However there is a rare juvenile form with onset before 6 years of age, also with a male predominance.
No studies have shown an increased incidence in specific racial groups.
Nodulocystic acne is associated with other follicular occlusion disorders particularly hidradenitis suppurativa.
The acne conglobata variant of nodulocystic acne is the 'A' in a number of syndromes including: SAPHO, PASH, PASS, and PAPA.
What causes nodulocystic acne?
The pathogenesis of acne is believed to be multifactorial involving increased sebaceous gland activity, abnormal keratinisation of follicles, the action of microorganisms, and subsequent inflammation.
Specific risk factors for nodulocystic acne include:
- Genetic factors
- Drugs including anabolic steroids, etanercept, imatinib
- Dietary supplements such as whey
- Haemodialysis.
What are the clinical features of nodulocystic acne?
- Solitary or multiple inflammatory nodules and pseudocysts
- Firm, fluctuant, and/or tender
- Involvement of the face, neck, and trunk
Nodulocystic acne
More images of acne ...
What is acne conglobata?
Acne conglobata is a rare severe form of nodulocystic acne. It presents with groups of multiple comedones and inflammatory papules, pustules, and nodules involving the trunk, limbs, and buttocks. Interconnecting abscesses and draining sinuses become secondarily infected causing pain and malodour. Healing is slow, leaving unsightly hypertrophic and atrophic scars. Acne conglobata is often very persistent, lasting into the 30s or 40s.
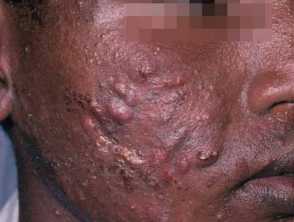
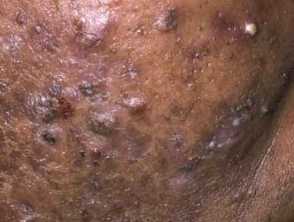
How does nodulocystic acne present in different skin types?
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and keloid scarring are common complications of nodulocystic acne in skin of colour.
What are the complications of nodulocystic acne?
- Psychological effects of acne
- Keloid, hypertrophic and atrophic scars
- Pyogenic granuloma
What is the differential diagnosis of nodulocystic acne?
How is nodulocystic acne diagnosed?
Nodulocystic acne is a clinical diagnosis. Hormone studies may be considered in the presence of suggestive clinical features.
What is the treatment for nodulocystic acne?
Topical treatment is usually ineffective for nodulocystic acne.
The recommended treatment is oral isotretinoin which should be commenced early to prevent scarring. Treatment is required for at least five months, and further courses are sometimes necessary. Intralesional steroids following cyst drainage, can be used for individual persistent or large inflammatory nodules or cysts.
Patients with acne conglobata often need additional treatments, such as:
- Oral antibiotics for secondary bacterial infection
- Systemic corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Adalimumab, used off-label, for resistant severe disease .
What is the outlook for nodulocystic acne?
Nodulocystic acne typically persist into adult life. Unless treated early and effectively, nodulocystic acne results in scarring particularly on the torso.