Introduction
Actinic granuloma is also known as O’Brien granuloma.
Actinic granuloma is thought to be an inflammatory response to extensive sun damage with subsequent degeneration of elastic fibres. It begins as flesh-coloured or pink papules which coalescence into annular plaques.
Histology of actinic granuloma
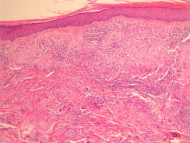
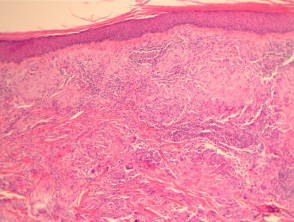
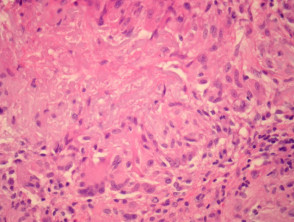
In actinic granuloma, sections show a granulomatous reaction involving the markedly elastotic dermis (figure 1). The giant cells contain elastic fibres and may be of the foreign body type (figure 2). There is a mixed associated infiltrate.
Actinic granuloma pathology
Special stains in actinic granuloma
Elastic stains show damaged elastic fibres that are engulfed by giant cells.
Differential diagnosis of actinic granuloma
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma – Lacks dense dermal elastosis, which is thought to be responsible for the granulomatous reaction. Some of these cases have been considered synonymous with actinic granuloma, which has caused some confusion with nomenclature.
Granuloma annulare – Elastotic debris is not present within the granulomatous reaction. Instead, there is necrobiosis and mucin deposition