What is autologous serum skin testing?
Autologous serum skin testing is an investigative test for autoimmune urticaria, which is a type of chronic urticaria. It is undertaken in specialist centres for some patients with chronic urticaria.
Normal immunoglobulin-E antibodies (IgE) activate IgE receptors (FceRI) on mast cells and basophils. These cells release histamine, an important mediator in allergic responses. Autoimmune urticaria is due to autoantibodies that bind to either these receptors or the IgE antibodies themselves. This causes inappropriate activation of the mast cells and basophils and release of histamine.
Autologous serum skin testing detects circulating autoantibodies, indicating an autoimmune origin in some patients with chronic urticaria.
When is autologous serum skin testing performed?
Inducible chronic urticaria can be detected when a certain stimulus provokes wealing, such as cold air in cold urticaria, or scratching the skin in dermographism.
Spontaneous or ordinary chronic urticaria may have no obvious stimulus. The autologous serum skin test may be a useful tool for diagnosis because it confirms those cases due to autoimmunity. If the test is negative, spontaneous chronic urticaria is considered idiopathic, ie, it has no known cause.
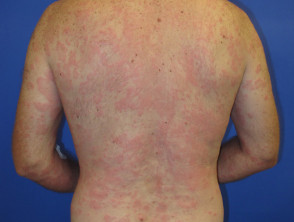
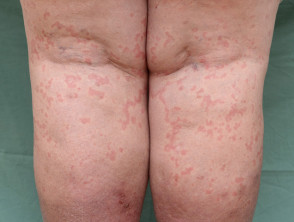
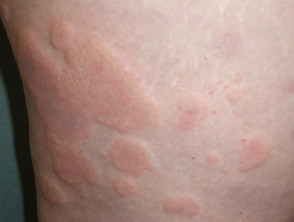
Chronic urticaria
Details of the procedure
The patient should stop taking antihistamines 2–3 days before autologous serum skin testing, to ensure that their urticaria is active at the time of the test. Immunosuppressive agents may also be stopped up to 3 months before the test.
The test should not be performed in an area of skin that has had weals in the past 24 hours.
- Two millilitres of the patient’s venous blood is taken, left to clot for 30 minutes, and then centrifuged to extract serum from the blood.
- A small sample of serum is injected into the underside of the patient’s forearm.
- Histamine is injected as a positive control, and saline water is injected as a negative control.
- There should be 5-cm gaps between each injection site.
- The response is recorded after 30 minutes.
A positive result occurs when the weal formed where the serum is injected has a diameter that is at least 1.5 mm larger than the saline weal.
What are the benefits of autologous serum skin testing?
Autologous serum skin testing is relatively reliable, with a sensitivity of 70% and a specificity of 80%. It is inexpensive and straightforward to administer.
What are the disadvantages of autologous serum skin testing?
Autologous serum skin testing should be undertaken by an experienced investigator; a poor technique can lead to false positive or false negative results.
The test is not standardised, with various methods described in the literature and different criteria for a positive result.
Positive results may occur in patients that do not have chronic urticaria, for example:
- Patients with autoimmune thyroid disease
- Up to 80% of children with allergic or non-allergic respiratory symptoms
- Drugs such as antihistamines, corticosteroids and immunosuppressant medications
Although a positive autologous serum skin test may indicate autoimmune urticaria, it does not reflect the severity of the disease.
What are the side effects of autologous serum skin testing?
Side effects are confined to injection site weals.