What is basal cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a common, locally invasive, keratinocytic, or nonmelanoma skin cancer. It is also known as rodent ulcer and basalioma. Patients with BCC often develop multiple primary tumours over time.
Basal cell carcinoma can be pigmented or nonpigmented. Its subtypes include:
- Nodular
- Superficial
- Morphoeic (also known as sclerosing and infiltrative)
- Other less common variants.
What are the clinical features of basal cell carcinoma?
The clinical features of basal cell carcinoma are:
- Slowly growing irregular nodule or plaque
- Skin coloured, pink, or pigmented
- Size varies from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter
- Spontaneous bleeding, erosion, or ulceration.
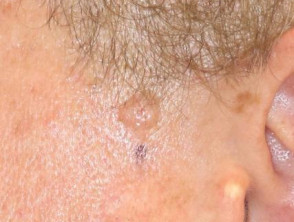
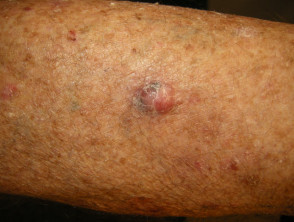
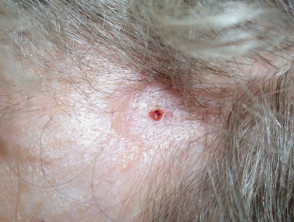
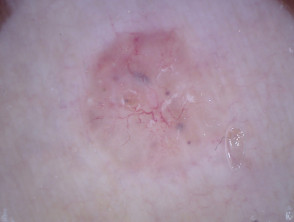
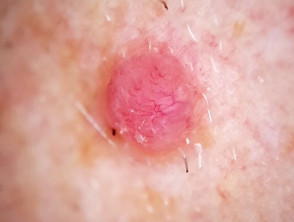
Clinical features of nodular basal cell carcinoma
Nodular basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of facial BCC. The clinical features of nodular basal cell carcinoma are:
- Shiny or pearly nodule with a smooth surface
- May have a central depression or ulceration, so its edges appear rolled
- Blood vessels crossing its surface
- The cystic variant is soft, with jelly-like contents.
Clinical features of nodular basal cell carcinoma
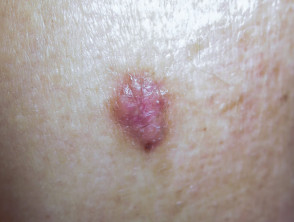
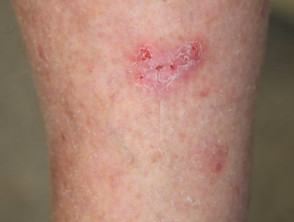
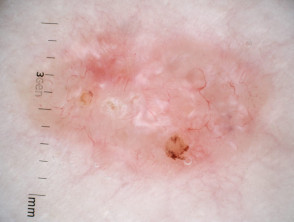
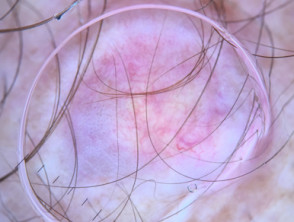
Clinical features of superficial basal cell carcinoma
Superficial basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of BCC in younger adults and is the most common type on upper trunk and shoulders. The clinical features of superficial basal cell carcinoma are:
- Slightly scaly, irregular plaque
- Thin, translucent rolled border
- Multiple microerosions.
Clinical features of superficial basal cell carcinoma
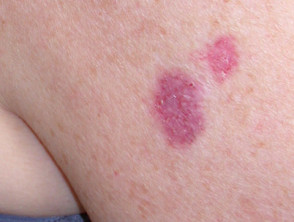
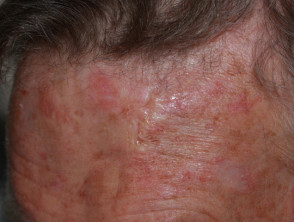
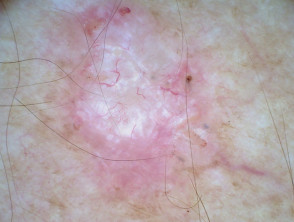
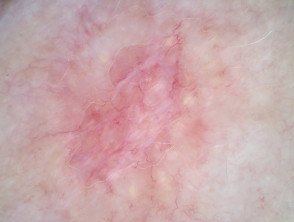
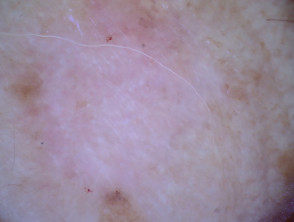
Clinical features of morphoeic basal cell carcinoma
Morphoeic basal cell carcinoma, also known as morpheic, morphoeiform, or sclerosing basal cell carcinoma, is usually found in midfacial sites. It can have wide and deep subclinical extensions and may infiltrate cutaneous nerves (perineural spread). It presents as an indistinct, waxy, scar-like plaque with ill-defined borders.
Clinical features of morphoeic basal cell carcinoma
What are the dermoscopic features of basal cell carcinoma?
The dermoscopic features of basal cell carcinoma vary according to subtype.
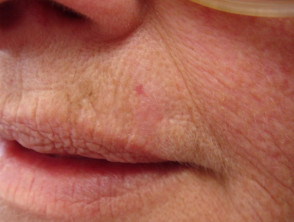
Pigmented basal cell carcinoma
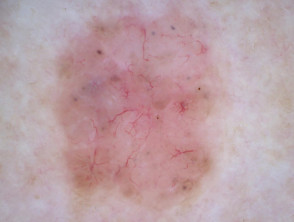
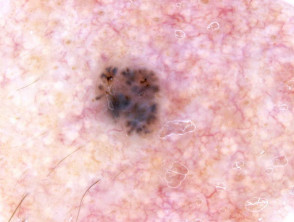
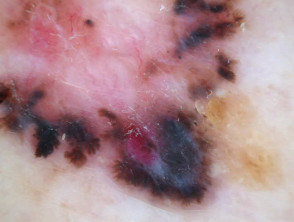
The dermoscopic features of pigmented basal cell carcinoma include:
- Absence of pigment network
- White, pink, grey, or light brown stroma
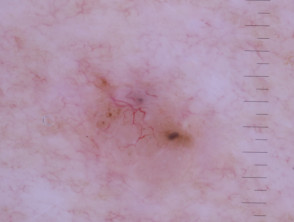
- Sharply defined, fine linear and branching serpentine vessels — these are also known as arborising vessels
- Structureless or leaf-like areas on the periphery of the lesion — these present as brown to grey-blue discrete bulbous blobs with pigment converging on a less-pigmented area
- Large blue-grey ovoid nests or blotches, also known as large clods
- Multiple blue-grey dots and clods
- Specks of brown and grey pigment (peppering, buckshot scattering)
- Concentric structures — dark central clod within a light brown larger clod
- Spoke wheel areas — these present as radial projections from a well-circumscribed dark central hub
- Short white lines or perpendicular white lines under polarised light only
- Focal ulceration
- Adherent fibre.
Branching serpentine vessels and blue-grey ovoid nests in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopy Branching serpentine vessels, leaf-like structures, blue-grey and brown dots in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopy Leaf like areas in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopy Leaf-like structures in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopy Adherent fibre, leaf-like structures and serpentine vessels in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopy Blue-grey ovoid nests in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopy Spoke wheels in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopy Perpendicular white lines, blue globule, leaf-like structures in pigmented basal cell carcinoma dermoscopyDermoscopy of pigmented basal cell carcinoma
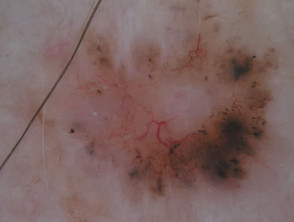
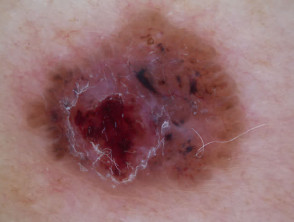
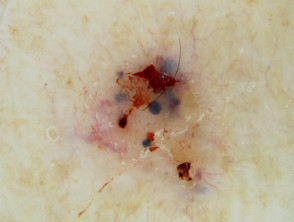
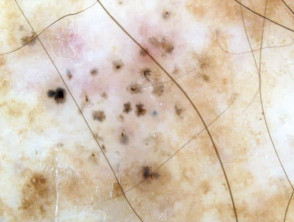
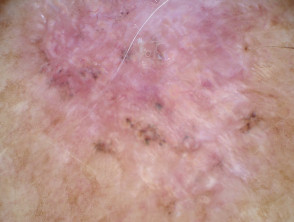
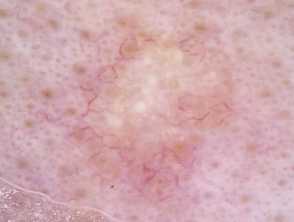
Nonpigmented basal cell carcinoma
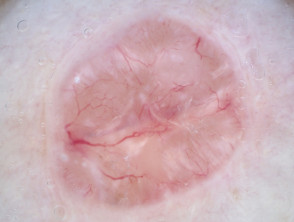
The dermoscopic features of nonpigmented basal cell carcinoma include:
- Bluish or whitish-pink stroma
- Asymmetrical branching serpentine (arborising) vessels
- Focal ulceration
- Slight scaling
- White clues, particularly perpendicular white lines (polarised light only) and structureless roundish white or yellowish areas.
On close inspection, some apparently non-pigmented basal cell carcinomas have a lightly pigmented stroma.
Nodular basal cell carcinomas lose the blue hue and instead may have a white rim around central ulceration. White clods (milia-like cysts may be present.
Dermoscopy of nonpigmented basal cell carcinoma
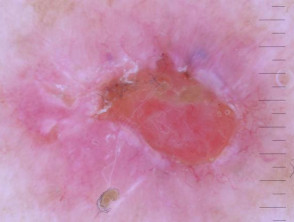
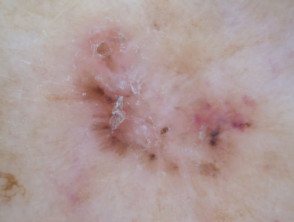
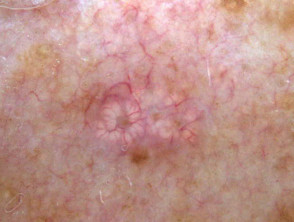
Dermoscopic features of nodular basal cell carcinoma
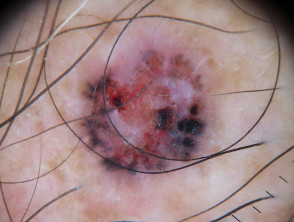
The dermoscopic features of nodular basal cell carcinoma include:
- Arborising vessels (branched red lines)
- Blue-grey ovoid nests (large clods)
- Ulceration
- Peppering (grey or brown dots) and or clods.
Dermoscopy of nodular basal cell carcinoma
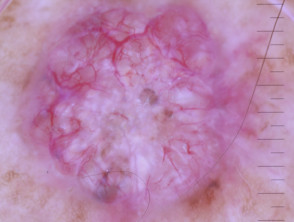
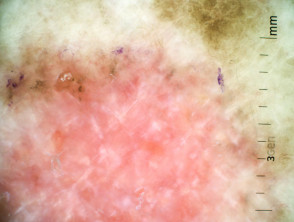
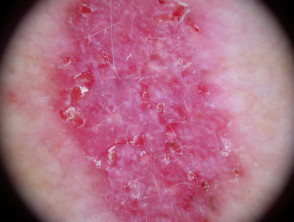
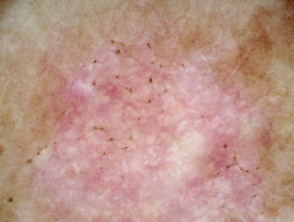
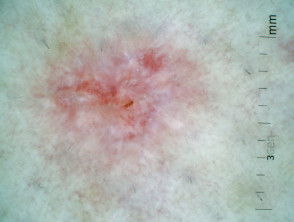
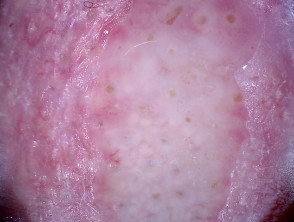
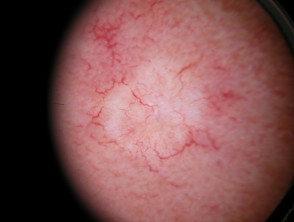
Dermoscopic features of superficial basal cell carcinoma
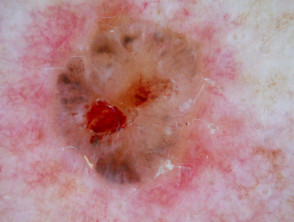
The dermoscopic features of superficial basal cell carcinoma include:
- Short fine telangiectases
- Perpendicular white lines (polarised light only)
- Ulceration and adherent fibre
- Leaf-like areas (brown to grey-blue discrete bulbous blobs that often form a pattern shaped like a leaf; they can sometimes appear as tan, broad, and fuzzy streaks at the periphery of a lesion)
- Absence of blue-grey ovoid nests, arborising vessels and ulceration
- Multiple small erosions
- White, red structureless areas (milky pink areas)
- Shiny white to red areas.
Dermoscopy of superficial basal cell carcinoma
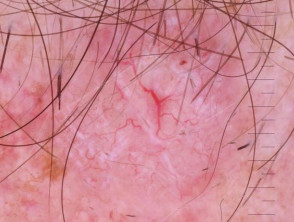
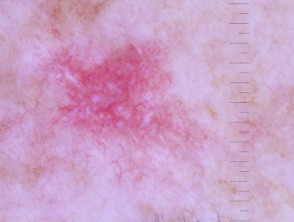
Dermoscopic features of morphoeic basal cell carcinoma
The dermoscopic features of morphoeic basal cell carcinoma include:
- A predominant white structureless scar-like area with a few fine branching serpentine vessels and multiple brown dots
- Sometimes vessels are the only clue.
Dermoscopy of morphoeic basal cell carcinoma
What is the dermoscopic differential diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma?
Differential diagnoses for basal cell carcinoma are:
- Sebaceous hyperplasia
- Melanoma
- Pilomatricoma
- Trichoepithelioma.
Dermoscopic differential diagnosis of BCC
What is the histological explanation of features of basal cell carcinoma?
Below are histological explanations for the features of basal cell carcinoma.
Sharply defined fine linear and branching serpentine vessels
Thickening of the epidermis causes dilated papillary dermal blood vessels (which usually appear as red dots) to be drawn out to form sharply defined fine linear and branching serpentine vessels. They sit close to the surface of the skin.
Leaf-like areas
Leaf-like areas are brown to grey-blue discrete bulbous blobs that form a pattern shaped like a leaf and are caused by nodules of pigmented basal cell carcinoma cells in the upper dermis.
Large blue ovoid nests
Large blue ovoid nests are also known as large blue clods and are created by nests of basal cell tumour in the dermis.
Multiple blue clods
Blue clods are formed by nests of basal cell tumour in the dermis.
Specks of brown and grey pigment
Specks of brown and grey pigment are formed as follows:
- Grey dots are due to melanin pigment within the papillary dermis, either free, in small nests of melanocytes or, more commonly, in melanophages
- Brown dots reflect either small nests of melanocytes in the basal epidermis, focal pigmented keratinocytic proliferation, as seen in some forearm solar lentigines or superficial dermal haemosiderin deposition.
Spoke wheel areas
Spoke wheel areas are also known as radial projections joined at a central hub and are formed by nests and proliferation of pigmented basal cell carcinoma cells.
Perpendicular white lines
Perpendicular white lines are thought to be caused by fibrous tissue.