What is achromic naevus?
Achromic naevus, also called naevus depigmentosus or hypochromic naevus, is a pale (hypopigmented) birthmark due to an abnormal clone of melanocytes with an impaired ability to transfer melanosomes to keratinocytes.
What are the clinical features of achromic naevus?
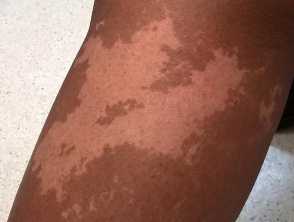
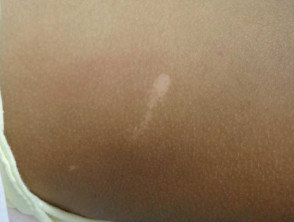
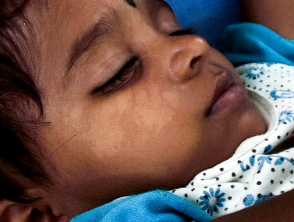
Achromic naevus presents in the neonate or early childhood period as a flat pale hypopigmented macule with a characteristic serrated border.
Clinical images of achromic naevus in skin of colour
What are the dermoscopic features of achromic naevus?
On dermoscopy, an achromic naevus appears as a white structureless area with an irregular serrated border and pseudopod-like extensions. There is a faint but normal reticular pigment background throughout. Hairs within the lesion are of normal colour with perifollicular pigmentation. Pigmentation in the surrounding skin is normal with no hyperpigmented border.
Dermoscopy images of achromic naevus in skin of colour
What is the histological explanation of the dermoscopic features of achromic naevus?
The histology of achromic naevus shows a normal or slightly reduced number of melanocytes with reduced melanosomes in the keratinocytes. The white structureless areas seen on dermoscopy of achromic naevus correspond with reduced melanin in the epidermal keratinocytes. The faint reticular pigment network indicates melanin remaining in the melanocytes.
What is the differential diagnosis of achromic naevus on dermoscopy?
- Vitiligo dermoscopy: milky white structureless area with a diffuse ‘white glow’ not seen in achromic naevus. Vitiligo has a well-defined border which can be hyperpigmented. The pigment network is usually absent. Hairs within the area are often white with loss of perifollicular pigmentation [see Dermoscopy of vitiligo].
- Pityriasis alba dermoscopy: poorly-defined pale area with fine surface scale, normal hair colour, and sometimes erythema.
- Ash leaf macules dermoscopy: seen in tuberous sclerosis, ash leaf macules can be distinguished from achromic naevus on dermoscopy by areas of reticular pigment network loss amongst the background of a faint pigment network.