DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages
Quiz
Acneiform eruptions – 12 cases
This quiz involves skin conditions similar to acne i.e. there are follicular papules and pustules. At times they may be difficult to distinguish from each other and from acne. Swabs and skin scrapings for microscopy, bacterial and fungal culture may aid diagnosis.
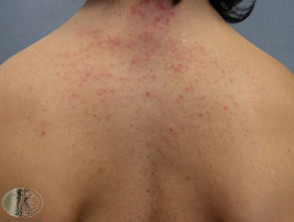
Acneiform eruptions may affect the face and neck. Acneiform eruptions on trunk are described as folliculitis, which may be due to infection, obstruction, or unknown irritant factors. Time course, distribution and appearance may be helpful in making a more accurate diagnosis.
Superficial staphylococcal folliculitis is often accompanied by deeper furunculosis (boils) and abscesses. Individual lesions are acute, tender, follicular pustules. Staphylococcal follicular pustules may also be seen in wound infections. In contrast, pustules accompanying impetigo are non-follicular and less symptomatic. Mild infections resolve without treatment, but topical antiseptics / antibiotics or oral flucloxacillin may be required for more troublesome infection. The quiz describes non-staphylococcal folliculitis.
For each of the twelve cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately 2 minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
Case 10
Sign up to the newsletter
© 2024 DermNet.
DermNet does not provide an online consultation service. If you have any concerns with your skin or its treatment, see a dermatologist for advice.