DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages
Quiz
Mixed diagnoses – 10 cases (7 of 11)
For each of the ten cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately five minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
When you finish the quiz, you can download a certificate.
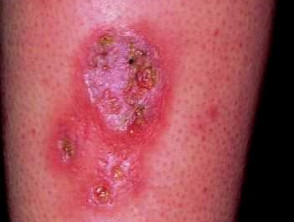
Case 5
A 16-year-old female presents with an area of relatively painless ulceration on her shin, which has arisen following a mild injury several months earlier.
Sign up to the newsletter
© 2024 DermNet.
DermNet does not provide an online consultation service. If you have any concerns with your skin or its treatment, see a dermatologist for advice.