Introduction
Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma is an uncommon variant of fibrohistiocytic tumor with intermediate malignant potential (metastases are rare but do occur). Typical cases occur in young adults and most often present in the skin or soft tissue of extremities or neck.
Histology of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma
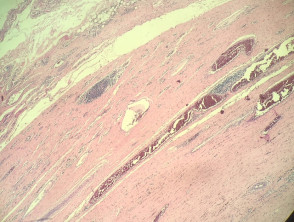
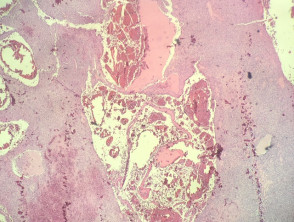
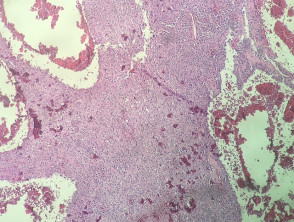
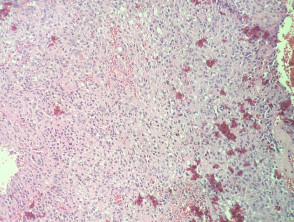
In angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma, the histopathology shows a dense capsule surrounding the tumour and associated lymphoid aggregates (figure 1). Centrally, there are large blood filled cavities associated with surrounding haemorrhage and hemosiderin deposition (figures 2,3). In other areas, there is a solid growth of monomorphic bland spindle to ovoid eosinophilic cells (figure 4). In some areas there may be some pleomorphism and mitotic activity.
Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma pathology
Special studies for angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma
Immunohistochemistry shows the tumour cells are positive with CD68. Variable positivity can be seen with actin, desmin, CD99, and EMA.
Cytogenetically, these tumours almost invariably show a translocation with FISH studies (usually t(12;16)(q13;p11).
Differential diagnosis for angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma
Other conditions that should be considered in the differential diagnosis of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma include:
- Fibrous histiocytoma (dermatofibroma) — these can have some large vascular spaces (eg, the aneurysmal variant). However, the classic features of a thick tumour capsule and lymphoid aggregates are absent
- Sarcoma — given the foci of atypia that may be present, a battery of immunohistochemical studies and cytogenetic studies may be needed to rule out a higher grade malignancy. The capsule and inflammatory changes are unusual in other tumours.