What is circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis?
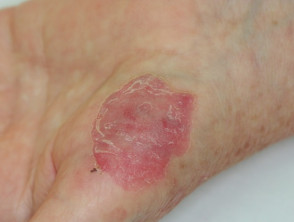
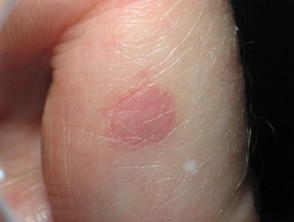
Circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis is a rare, persistent, solitary, red patch of thin skin on the hand.
Who gets circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis?
About 50 cases of circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis have been described in the medical literature to date. It predominantly affects women in the 4th to 7th decade of life. A congenital case has been described.
What causes circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis?
The cause of circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis is unknown.
- One case reported an association with human papillomavirus (HPV) type 4, which is a cause of viral warts, but the significance of this finding is unclear.
- A localised loss of cellular adhesion is possible, causing the abrupt loss or shedding of the stratum corner (horny) layer of the epidermis.
- Abnormal keratinisation or abnormal keratinocyte differentiation have also been implicated.
- A couple of cases have been associated with trauma (and were called “pseudo-circumscribed palmar/plantar hypokeratosis).
What are the clinical features of circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis?
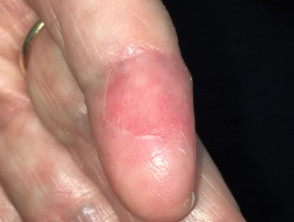
Circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis most commonly arises on the thenar or hypothenar eminence of the palm, the sole of the foot (plantar aspect) or less commonly the palmar aspect of fingers. Very rarely it can affect the skin of the dorsum of the fingers or non-acral sites of skin. There are a few reports of cases with more than one lesion affecting both palms or palms and fingers or palms and soles.
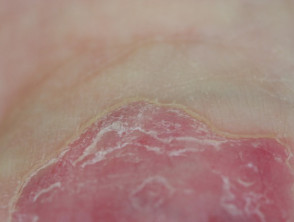
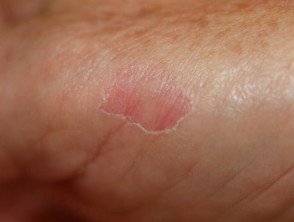
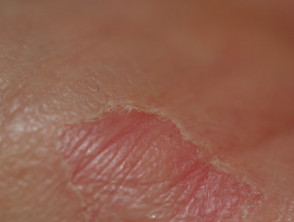
Circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis has a central pink area of thin atrophic, smooth or slightly scaly skin, while at the edge there is an abrupt transition to normal skin.
Circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis
How is circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis diagnosed?
Circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis can be diagnosed on its distinctive clinical appearance.
A biopsy may be taken across the edge of a lesion. This shows the epidermis in central area of affected skin lacks stratum corneum (horny layer). At the edge of the lesion there is a very sharp abrupt transition to the normal compact orthohyperkeratosis typical of palmar skin. There are no histological findings to suggest HPV infection.
The main differential diagnoses to consider in circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis are porokeratosis and squamous cell carcinoma in situ.
What is the treatment circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis?
No treatment is required for circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis. However:
- Regular application of topical calcipotriol (calcipotriene) 0.05% cream may flatten the sharp cut-off at the edge of the lesion, leaving a thin, flat, pink, patch of skin.
- 5 -Fluorouracil cream, cryotherapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT) have been reported to be partially effective in individual cases.
What is the outcome for circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis?
Circumscribed palmar hypokeratosis is a chronic condition which persists unchanged over time or may very slowly enlarge. There are no reports of cancer developing within the lesions.