Main menu
Common skin conditions
NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Hon A/Prof Marius Rademaker, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, 1999.
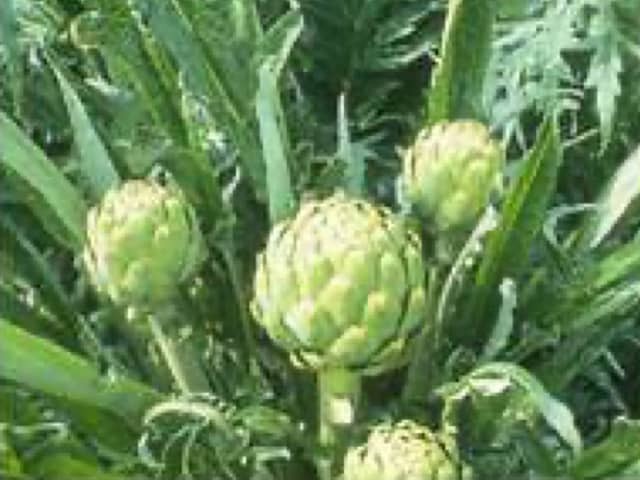
Common name: |
Globe artichoke |
Botanical name: |
Cynara scolymus |
Family: |
Member of the Asteraceae (Compositae) family |
Origin: |
It is widely cultivated in the Mediterranean. |
Description: |
Large thistle-like flower heads (up to 15 cm) surrounded by fleshy bracts. |

Uses: |
The buds are consumed as a vegetable. Also used for flower arranging. There is recent interest in a chemical extract of artichoke, silymarin (a flavanoid), as a possible cancer chemo-preventive agent. |
Allergens: |
The allergen in artichoke is thought to be Cynaropicrin. It seems to be released from cut stems and roots. |
Allergy: |
It is well recognised to cause hand dermatitis, particularly in pickers, market gardeners and flower arrangers. It is not known whether any of the allergen are found in the portion of the plant that is eaten, but there have been several reports of allergic rhinitis and asthma from ingested artichoke. Contact urticaria has also been reported following exposure to artichoke. |
Cross reactions: |
Other members of the Asteraceae (Compositae) family. |
Other information: |
Jerusalem artichoke is a different species (Helianhus tuberosus). |
Patch test: |